Professional version only
Probabilistic and Conditional Branching
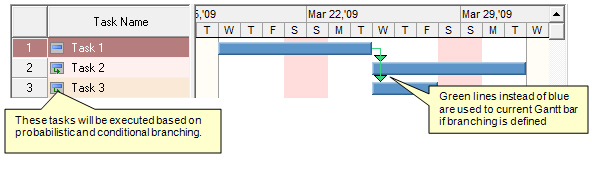
Creating probabilistic and conditional
branching
- Open the Task Information
dialog box for the task in which you want to create the branch.
- Click the Branching tab.
- For each successor define the Condition and
Value that will cause the successor to be
cancelled. The type of value you can select is dependent upon the
condition you select.
- Select the Action that will occur when a
successor is cancelled or executed.
- Select the This task and all successors are always
executed even if cancelled by predecessors check box if you
want to force this task and all successors to be run in the
simulation even if its predecessors are canceled. A task can
have multiple predecessors. These predecessors may belong to
different branches and can be canceled due to the results of the
branching. Select the check box if you want to force this task and
all successors to be run in the simulation even if its predecessors
are canceled.
- Click OK.
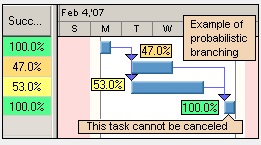
Example of Conditional and
Probabilistic Branching
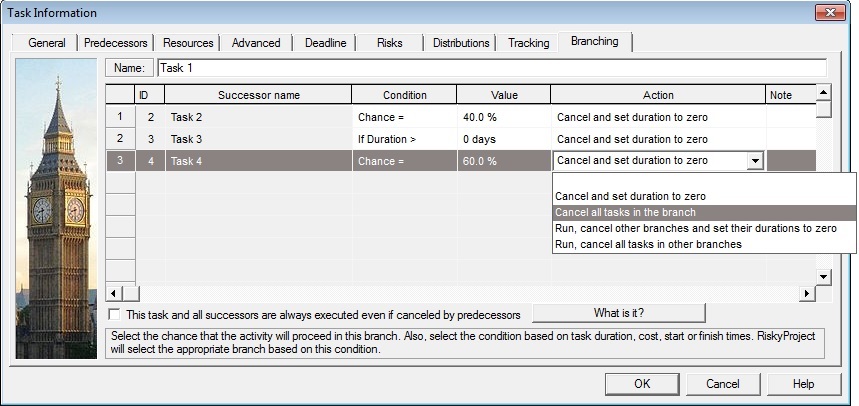
In this case, Task 1 has three successors:
- Task 2 will be canceled in 40% of the time. Task 2’s success rate will be around 60%. This is example of probabilistic branching
- Task 3 will be canceled if duration of Task 1 is greater than 5 days. Task 2’s success rate depends on the statistical distribution for duration of
Task 1. This is example of conditional branching.
- Task 4 and all it successors will be canceled in 60% of cases. Task 4 success rate will be around 40%. This is example of probabilistic branching.
You may use any risk assignment view or dialog to assign a
mitigation and response plan to a risk.
|




